Are IT Certifications Worth It? Plus Our Guide to the Top IT Certificates
Is it worth it for companies to encourage IT certifications for their technology employees? What certifications are organizations most interested in? Gaining competency in various areas helps expand the possibilities for your company's growth and an individual's job opportunities. If you're seeking a job in the IT industry, you want to know the best option to land the position you want.
Are IT Certifications Worth It?
Whether IT certifications are worth it depends on your business needs and which skills areas your workers may need to improve:
- Certifications can help people advance in their careers or find a better-paying position with another company
- Some industries require employees to be certified to meet regulations for HIPAA and avoid issues with GDPR and other privacy regulations
- An IT certifications list will narrow things down and help companies find the best one, as each certificate has unique pros and cons
Key Benefits and ROI Quick Facts
- Employers see measurable value: 97% of IT decision-makers say certified staff add value; ~1 in 5 estimate that value at $30K+ per year (Source: Global Knowledge)
- Career outcomes for candidates: 37% report salary increases and 27% report promotions after certifying (Source: Pearson VUE)
- Organizations invest more: 71% of candidates say their employer increased training budgets for certifications (Source: Pearson VUE)
- Confidence and productivity: Certified staff often deliver ~50% more value by bridging skills gaps (Source: CIO)
When Certifications Pay Off Most
- Early career / career change: Opens doors, proves baseline skills
- Closing skill gaps: Best when tied to a current or target role
- Regulated sectors: Some government/healthcare roles legally require certifications
Which Certification Is Best for IT Technology?
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates over 2 million people work in computer and information technology, many with specific concentrations. Around 98% of them focused on information systems, computer management, security, telecommunications or computer science. With so many people working in varied areas, figuring out the best IT certifications is challenging.
So, what IT certification should I get? Employees should start by talking to their current employer about opportunities for promotion. Management can discuss the future career plans of their workers and see what gaps they can fill to work their way up in the department. Certificates can benefit companies and individuals when approached strategically. Although the certifications you need will depend on your department's strengths and weaknesses, none is objectively better than the others.
You may also need to meet certain regulatory requirements via training and certification. There will likely be a few IT certificates that pop up repeatedly in your research. These are the ones most companies seek in their employees.
How to Choose the Right Certification
The following are some things to consider when choosing an IT certification option:
- Role-Fit: Link exam objectives to the description of the job you are targeting
- Market-Fit: Prioritize certifications consistently listed in top-paying surveys
- Cost and Time: Include exam fees, study time, and renewal cycle
- Progression: Choose certifications that act as stepping stones to more advanced ones, such as CAPM leading to a PMP for project managers
- Hands-On: Choose programs with labs/performance-based testing
What Certifications are Worth Getting for Information Technology?
Here is a list of certifications companies and IT professionals should consider. Gaining a certificate requires basic information technology skills as a building block:
AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner
Amazon's cloud-based systems work with big and small organizations to provide web hosting, storage and even a delivery system to sell software. Working within the Amazon Web Services environment is different from other cloud-based systems, so knowing the ins and outs requires training.
Those seeking AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner certification must understand how cloud computing works but don't necessarily need technical knowledge. Gaining a certificate shows employers an individual can communicate about working in the AWS environment and understand instructions.
Seeking certification ensures you'll understand basic IT services and how to utilize them on AWS Cloud. You'll also gain knowledge of AWS services, billing and pricing, overall security and how a business improves by using the cloud. The exam costs $100, and it takes about 90 minutes to answer 65 multiple-choice questions.
Organizations with AWS-certified employees will experience improved communications and fewer misunderstandings. Since it's a popular cloud platform, the knowledge often transfers from one job to the next.
Quick Notes
- Who it's for: Beginners and non-engineers who need cloud literacy
- Time and cost: ~$100; 65 questions, 90 minutes
- Renewal: Valid 3 years
- What it proves: Baseline AWS cloud fluency and terminology
Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
Testing your systems to ensure hackers can't easily get through shores up your security and protects crucial digital assets. Rather than hiring a third party to find weaknesses, enlist the help of one or more internal workers to probe your system for vulnerabilities.
Certified Ethical Hacking certification takes the knowledge your IT department already has and teaches workers more legal and ethical techniques they can use. CEH certification starts with understanding what employees should and shouldn't do while hacking your systems, even for tests. Individuals with this type of training stay out of trouble and add value to the brands they serve.
A CEH certificate leans toward a firm understanding of the network security framework. It's an intense certification for which you'll need to develop new skills. However, the effort is worth it as employees gain skills that help protect the company they work for now and in the future.
Quick Notes
- Who it's for: Security analysts, pen-testers
- Time and cost: Varies widely — ~$950–$1,200 for exam-only, or $1,699–$3,499+ with EC-Council training packages and bootcamps
- Renewal: Every 3 years via continuing education credits
- What it proves: Ability to legally/ethically identify vulnerabilities
CISM
CISM stands for Certified Information Security Manager. To earn your CISM credentials, you need five or more years of information security experience and a minimum of three years of information security management and other practice analysis.
You must gain experience first, so you'll need some information management knowledge ahead of time. The process is challenging but ensures only those with the proper training and credentials are ready for more rigorous responsibilities.
Your organization's cybersecurity is one of the most crucial aspects of your business. CISM then may be one of the best cyber security certifications to ensure only those most qualified manage your security. Your team will gain credibility and improve efficiency, proving the value of IT certification.
Quick Notes
- Who it's for: Security managers with 5+ years' experience
- Time and cost: ~$760; rigorous application process
- Renewal: Annual maintenance required -- 20 CPEs each year (120 over 3 years) plus an annual fee
- What it proves: Governance and leadership in cybersecurity programs
CISSP
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) gives you the authority to be a cybersecurity expert. Similar to CISM, candidates for this IT security certification must have five years of experience in the field. A four-year college degree satisfies one year of the requirement.
Getting credentialed in cybersecurity protects your organization from cyberattacks and adds legitimacy to your IT team.
Quick Notes
- Who it's for: Experienced cybersecurity professionals
- Time and cost: ~$749; 3-hour exam
- Renewal: Every 3 years via continuing credits plus annual fee
- What it proves: Advanced security expertise across the 8 CISSP "domains"
CompTIA
CompTIA certification is another acknowledgment. According to CompTIA their A+ certification is the industry standard for launching IT careers. They offers many different types, from general IT support (A+) to networking (Network+) and security (Security+). A+ is entry-level support, not a security cert; Security+ is typically the baseline for many junior security roles and some public-sector requirements.
Passing the tests isn't enough to land a job, though. Employers want to know how you apply the knowledge you've gained in real-life situations. CompTIA has no prerequisites, but the organization does recommend two years of experience in IT management and security before taking the exam.
Quick Notes
- Who it's for: Entry-level IT (A+), networking (Network+), security (Security+) (examples)
- Time and cost: Vary depending on the exam
- Renewal: Every 3 years
- What it proves: Baseline IT support, networking, or security knowledge
ISACA
The Information Systems Audit and Control Association offers IT security certifications like the COBIT framework, CRISC, CGEIT, CET and ITCA. The group's purpose is to help tech professionals and their companies understand the positive potential of technology.
Prerequisites vary depending on the information security certifications your employees seek. Finding a place where workers can take multiple exams and learn simultaneously saves you time and effort and ensures you obtain all the necessary skills.
Quick Notes
- Who it's for: Audit, risk, and IT governance professionals
- Time and cost: Varies
- Renewal: Every 3 years via continuing credits plus annual fee
- What it proves: Risk, audit, and IT governance expertise
ITIL
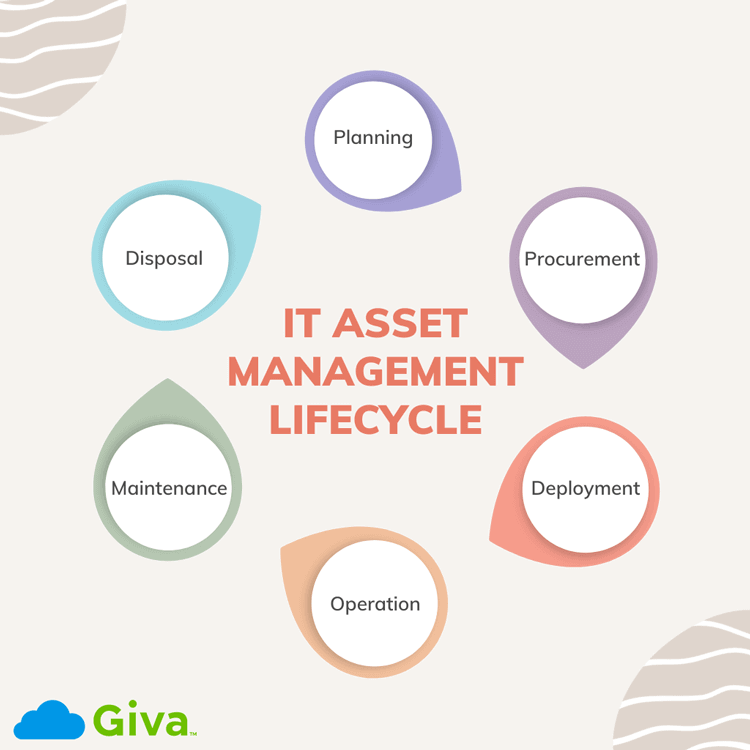
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL®) sets forth some basic practices for IT Service Management and asset applications. Learning how to best use the framework benefits any brand creating digital goods and services.
The ITIL 4 Foundation helps people learn about the ITIL framework in networks and certifies professionals in its use. ITIL is used from development to delivery for creating and improving tech products and services for the public.
Certification focuses on using the framework and tapping into the resources library. The exam has 40 multiple-choice questions and takes about 60 minutes. To gain certification, you must answer 26 questions correctly.
Quick Notes
- Who it's for: IT service managers and process owners
- Time and cost: Varies widely; 40 questions, 60 minutes, 65% pass mark
- Renewal: Every 3 years
- What it proves: Understanding of ITIL service management framework
CAPM
While many certifications focus on technology, IT departments need project leaders as well. CAPM is the Certified Associate in Project Management certification offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI). It's an entry-level program that builds foundational knowledge and skills for leading project teams. It also focuses on Agile principles and business analysis.
Candidates are required to obtain 23 contact hours of project management education before applying. This can be fulfilled using an Authorized Training Partner.
Lastly, a CAPM certification means automatically meeting the 35 hours of project management education and training required to sit for the advanced Project Management Professional (PMP) exam.
Quick Notes
- Who it's for: Entry-level project managers
- Time and cost: ~$225–$300; 3-hour exam
- Renewal: 15 Professional Development Units (PDUs) every 3 years
- What it proves: Foundational project management knowledge
Brief Salary Outlook and High-Value Certifications
Cloud and security credentials continue to top global salary surveys. For instance, AWS Certified Security–Specialty holders report ~$200K annually, while Google Cloud Professional Architect averages ~$190K. These don't guarantee earnings but signal strong employer demand. See more information on these from the Skillsoft page.
Limitations and Caveats to IT Certifications
As always with benefits, there can be caveats. Here are a few regarding IT certifications:
- No automatic job guarantee: Certifications open doors but don't replace experience
- Exam-focused: Some argue they overemphasize test preparations vs. real skills
- Renewal costs: Many require recertification every so-many years
Business Benefits of IT Certifications for Employers
Beyond individuals or employees themselves, there can be a benefit to the employers of certified personnel, such as:
- Certified staff close skill gaps faster and improve team efficiency
- Companies see ~$30K in additional annual value from certified employees (Source: Global Knowledge)
- In regulated industries, baseline certifications are mandatory to meet compliance requirements
The Final Word for IT Certifications
The above list of IT certifications should help you determine what's best for your company.
Stay inside the parameters of GDPR and other privacy regulations, including HIPAA or HITECH. Check out how Giva's certifications page digs into the details of crucial employee training and provides information on good IT certifications to have.