Knowledge Management is a Practice many organizations want to implement but only sometimes accomplish. Then, when Covid-19 hit and offices went virtual, new challenges besides technology disrupted business as usual. At the top of the list of challenges was knowledge sharing. Asking your neighbor a "how to" question was difficult.
Sending people home brought chaos. Besides accommodating a spike of remote logins, scattered workforce productivity dropped because of inadequate information systems that typically drive employees to seek answers from colleagues. Forrester consulting found that 35% of knowledge workers say that individuals hold most of the information in their organizations and that what knowledge documentation there is, is hard to find.
Covid-19 may have been the tipping point, but the knowledge transfer cause hindering optimal productivity has been around for years:
- Organizations are too large to know who might have the answer to your question.
- Workers don't know who to contact quickly when a problem arises.
- Many organizations have inefficiencies in current Knowledge Management systems, such as outdated knowledge and poorly formatted knowledge articles.
- Knowledge silos prevent knowledge from flowing easily between teams and networks.
- Hybrid working models further hamper this, which makes it harder for employees to connect with coworkers.
The scary part is that 63% of employees say they spend too much time searching for the right people or information to help them. When business leaders view their knowledge transfer strategy and have thousands of employees, wasted time can amount to significant productivity costs (i.e., revenue) for an organization.1
Google is an example of a knowledge company, with 5.4 billion Google searches per day.
"Google's mission statement is to organize the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful."
Do you Google? If so, you are searching and using the knowledge you did not have before you click search. Google has set a high bar for knowledge transfer. No wonder your workers expect more from your business Knowledge Management team.
What ITIL Knowledge Management is and why it should be a business imperative is the topic of this article.
The purpose and objectives of ITIL Knowledge Management
"The purpose of the Knowledge Management (KM) Practice is to maintain and improve the effective, efficient, and convenient use of information and knowledge across the organization."2
The objectives of Knowledge Management3
- By ensuring that trustworthy and secure knowledge, information, and data are accessible throughout the service lifecycle, management decision-making will be improved (e.g., Strategy, Design, Transition, Operations, and Continuous Improvement).
- Assist the service provider in being more effective and raising the standard of services.
- Ensure that everyone on staff understands the importance of their service to clients.
- Keep access control for knowledge, information, and data that is appropriate for each audience in your Service Knowledge Management System (SKMS).
- Collect, examine, archive, distribute, use, and upkeep knowledge, data, and information across the service provider's organization.
Knowledge Management's business value4
KM provides value to every part of the organization:
-
KM increases Service desk productivity:
- Increase in agent productivity.
- Reduced aversion to web self-service (i.e., automated knowledge transfer to the user).
- Fewer escalations that result in lower costs and increased Customer Satisfaction (CSAT).
- Quicker evaluations of opportunities and solutions to problems.
- Maximum utilization of expertise from hard-to-find experts.
- Enables improvement using this platform.
- Compliance with statutory requirements as well as other criteria, such as written business policies, professional conduct guidelines, IT visions, and quarterly targets.
- Requirements in writing for the preservation of each type of data, knowledge, and information.
- Types of defined data, knowledge, and information that are simple for the organization to use.
- Maintaining accuracy, completeness, and validity of data, information, and knowledge.
- Providing people data, information, and knowledge as needed.
- Data, information, and knowledge disposed as necessary.
- Setting standards through templates for different types of knowledge, doing searches, and document creation conforms to best practices in storage and retrieval.
- Minimizing the likelihood and effects of employees leaving along with their knowledge.
- Faster training and onboarding of new employees.
- Improvement in staff morale and motivation given the better accessibility of work.
- Better results at the customer level.
- Improved customer service across speed, cost and quality.
If you have been paying attention, you noticed that every one of these points has a significant cost-savings and customer-satisfaction component. No other ITIL Practice has as many immediate Returns on Investment (ROI).
Benefits of Knowledge-Centered Service (KCS) Management
Knowledge-Centered Service (KCS) is about shifting IT focus from a few knowledgeable senior employees or groups to using knowledge as a strategic asset owned and maintained by the team. The team's main goal is to develop collective knowledge rather than only answer specific customer problems and increase organizational learning.
A Knowledge-Centered Service strategy seeks to:
-
Reward learning, collaboration, sharing, and improvement.KM is a company-wide endeavor to bring everyone together for knowledge transfer. It can only succeed and produce an ROI through top management's focused and unrelenting support. For KCS to work, management must create a KCS environment that supports the use of and creation of knowledge.
-
Create content as a by-product of solving problems, not from different creative activities, just to create knowledge articles.For instance, if you were a Service Desk agent who worked a particularly problematic case and needed help finding something in your KM system. You asked fellow Service Desk agents, and they were unable to help. When you finally resolve the incident and the user is happy, and after finishing documenting the incident, create a knowledge article right from the incident so that no one has to go through this struggle again. Just click and transfer to KM.
-
Evolve content based on demand and usage.KM is organic, which by definition is day-to-day needs that build the database one article at a time. There are better ways to do it than having IT technicians pounding out knowledge base articles. It is important to remember that there are no KPIs for the number of articles created. KPIs are for using knowledge articles to resolve something or do it in a shorter time to increase CSAT and lower costs.
-
Create knowledge bases based on an organization's collective experience so far.Growing your knowledge articles happens sporadically. It is not helpful to pressure people to create knowledge when it is inappropriate.For example, you should correlate article creation as necessary steps for each new release of an application. It then tapers off to nothing until the next release.New KM articles are a suitable feedback mechanism for the service transition project team. They must learn that knowledge creation is part of new application projects (release and deployment). Both the Service Desk and users should have access to instructions and training to avoid issues during early life support.
What performance metrics can you expect with a consistent KM Strategy?
According to the Consortium for Service Innovation:
- 50-60% improved Service Desk time to resolution.
- 30-50% increase in First Contact Resolution (FCR).
- Improved customer success and use of self-help knowledge.
- Service Desk cost savings of up to 50%.
- 70% improved time to proficiency (i.e., new hire training).
- 20-35% improved employee retention (i.e., less turnover).
- 20-40% improved employee satisfaction.
Service Transition life-cycle is the perfect home for KM
There are five ITIL life-cycle stages: Strategy, Design, Transition, Operations, and Continuous Improvement. Transition is the natural home for KM because it is the home of Change, Release, Configuration, and Deployment. These Practices are all transitional, introducing new services into the environment. KM will enter knowledge about the new release, answer questions that the Service Desk may field, and guide the operations supporting the new service. Users, Service Desk, and support staff benefit by having easy-to-find answers to help the new and modified services. In addition, employees benefit by knowing how to use the new service, increasing productivity and user satisfaction.
A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) of Knowledge Management is a decrease in questions fielded by the Service Desk during the early life support of deployment. Therefore, deployment teams should use the Service Desk team to review the knowledge articles. It is for them, after all.
Basic concepts of ITIL Knowledge Management
KM is more than just a database. KM provides context.
Types of organizational knowledge5
-
Explicit:
- Knowledge that is explicit is simple to record, convey, present, comprehend, and apply.
-
Examples of explicit knowledge:
- Customer data
-
Step-by-step instructions:
- Work instructions.
- How to audit an incident or service request.
- How to accurately categorize an incident.
- How to do the proper incident matching.
- How to execute a standard change.
- How to conduct a Post-Implementation Review (PIR) after a change (i.e., knowledge learned).
- How the Service Desk should correctly document an incident escalated to a Level 3 team (specific for the service and team).
- Employee survey responses
-
Tacit knowledge:
- Putting tacit knowledge into words is better when learning comes from observation.
-
Examples of tacit knowledge include:
- How Service Desk agents can create informative and fun how-to videos in answer to common service requests.
- A Service Desk agent's knowledge of how to approach and engage with an unhappy or demanding user.
- How Level 2 or 3 tech staff can best handle a call directly from a user even though the SLA says users must use the Service Desk as the Single Point of Contact (SPOC)?
- How a Service Desk agent can convey to a user that their call is a Priority 3 when the user insists it is a Priority 2.
- A Level 2 or 3 approach to a user interruption to install a quick fix.
- How to explain to a new employee the value of Knowledge Management.
- Share this experiential knowledge through video demonstrations and audio recordings since words alone often cannot adequately convey it.
-
Implicit knowledge:
-
Explicit and implicit knowledge combined:
- It isn't readily apparent. Often used without the individual being aware of using or thinking about it.
- It is simple to document and share knowledge with new users once the user has identified it.
- This second-nature knowledge becomes apparent by looking inwardly or when you have new employees by asking them to observe and document.
-
Explicit and implicit knowledge combined:
-
Tribal knowledge:
- A part of implicit knowledge that emphasizes the pooled experience held by your team.
- Typically, information is shared during casual interactions and discussions. Almost usually, the passing moments are rich in important information and insight. By sharing and documenting, the team gains.
The Data, Information, Knowledge, Wisdom (DIKW) model of Knowledge Management6
Data is a set of discrete facts
- The data is highly structured (e.g., incidents, requests, problems)
- KM stores data in enormous amounts (e.g., incidents, requests, problems, changes, configurations (CMS), events, and assets).
- The data must be 100% accurate and comply with QA standards (i.e., audits).
Information comes from providing context to data
-
Information gets stored as semi-structured content:
- Documents
- Multimedia
- KM activities to make it simple to record, search for, locate, reuse, and learn from experiences to prevent making the same mistakes again.
- For example, the average time to close Priority 2 incidents (i.e., combine data from start time, end time, and priority from a large data sample).
Knowledge is dynamic and context based
- Comprised of people's implicit experiences, thoughts, insights, attitudes, and judgments.
- Provides information in a format that's simple to use.
- Makes decision-making easier.
- For instance, since a new version of the service was introduced, the time it takes to resolve Priority 2 events has increased by 10%.
- And, using the knowledge tool with articles created by the infrastructure team, the number of escalation errors has decreased by 46% in the last month.
Wisdom makes use of knowledge to create value
- Value is produced by making smart choices based on information.
- It requires the ability to apply and be aware of context in order to make sound common sense decisions.
- For instance, inadequate documentation for the new version of the service is to blame for the lengthened time it takes to resolve Priority 2 incidents.
ITIL DIKW graphic7
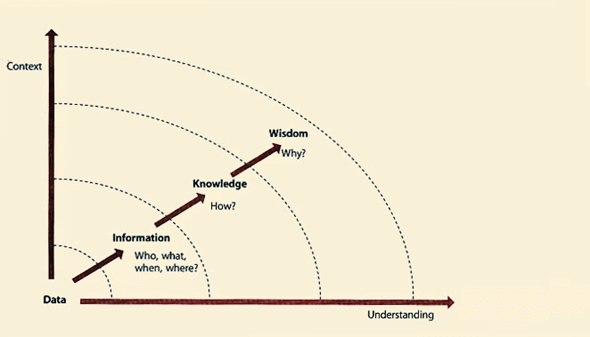
Everything depends on creating and collecting accurate data. For example, if incidents do not contain a valid service name and short description, everything fails in the Incident Management Practice. For KM to have value, the inputs must be 100% accurate. Incident audits are the key to incident ticket accuracy. The KM Practice should help the different teams create their audits. Reporting on error reduction is an excellent way to promote improvements.
Data accuracy is critical for KM — start by auditing
The following diagram is an ITIL value stream for Incident Management. It is more effective to audit between essential steps than wait and audit only at the end. By waiting until the end, the mistakes compound, and it is more difficult to pinpoint the moment of the error. Incident Managers at all levels of the value chain should agree on what a quality documented incident is for their department. It is not complicated or time-consuming.
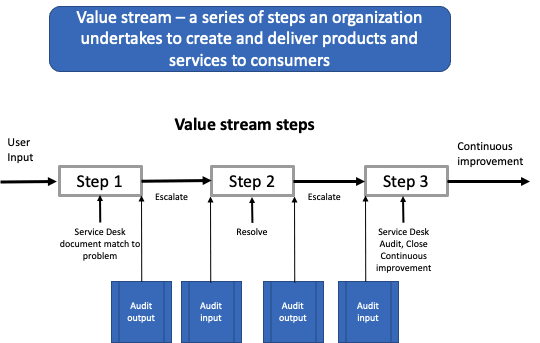
What does quality look like at the end of user input at the Service Desk? Create a checklist with inputs from Levels 2 and 3. For example, the ticket has the correct service affected by the incident, and the short description is perfect. Problem Management will thank you because the problem database will also be accurate through incident matching. Incident matching is another audit point. ITIL's best practices say all incidents should link to a problem.
Typically, the audit form takes no more than 90 seconds to complete the checkoff. In the diagram, this is the audit after step 1.
When the escalated team receives the ticket, the next level checks the Service Desk work and does an even faster audit. If there are errors, the next level documents the errors in the incident field called improvements (i.e., feedback). Also, they use a check field titled "Please Review." That way, the Service Desk runs a daily incident query to show them all "Please review" tickets, and the Service Desk agents use this for continuous improvement.
There are several reasons for these audits. First, we want to eliminate receiving any requests with errors. If there are input errors, it is likely to create more errors based on poor input. Avoid this waste!
In a learning organization, feedback is the best way to increase throughput and create higher-quality output.
Level 2 or 3 performs an audit once they resolve the ticket. They perform this audit to validate that all the new resolution data entered meets their department's quality standards. After the audit, the higher level resolves the incident and sends it back to the Service Desk for closure per Incident Management directives.
The Service Desk, specifically the agent that created the incident, the incident owner, completes the last audit before closing the ticket and notifying the user. The closed ticket is not in the realm of KM.
In only a few weeks, you will see the difference.
Repeating actions become habits. Habits increase speed and accuracy. As a result, data in the incident database and the Knowledge Management systems are perfect and valuable. Use a similar procedure for all data collected by KM.
The Service Knowledge Management System (SKMS)8
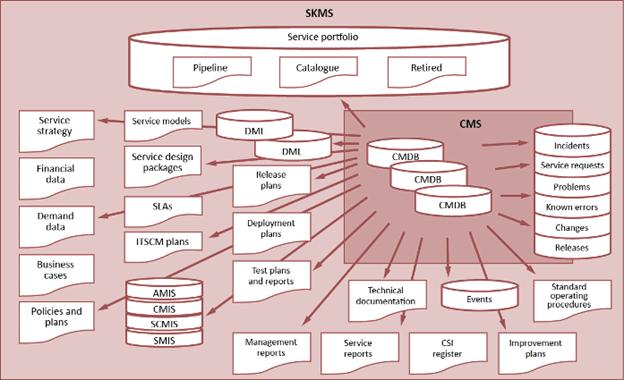
This diagram is an excellent example of how inclusive KM is. KM provides a portal that links many databases together. The portal allows you to look at one or multiple sources simultaneously. For example, if you were a service manager of the SAP Purchasing application and wanted to know the health of the service.
You would enter a query into the SKMS to show how your service has been doing over the last quarter.
You would get a report like this:
- # Incidents
- # Service requests
- # Problems
- # Known errors (KEDB)
- # Changes
- # Releases
- # Deployments
- Release and deployments in the planning stage
- Improvement plans
- Suggestions in the CSI register
- Availability plans and strategy (AMIS)
- Capacity plans and strategy (CMIS)
- Service continuity plans and strategy (SCMIS)
- Security plans and strategy (SMIS)
- User survey results
- Suggestions for improvements (CIR)
We could go on and on with this tool that allows you to know what is going on in the many areas of Service Management. KM is not something to do once you become mature. You use it now to get more mature quicker.
Why should a company adopt KM early?
We just made a bold statement not to wait to do KM. The primary reason is that IT is constantly collecting data. IT staff are always writing information articles such as:
- SLAs
- Work instructions
- Change Management Post-Implementation Reviews (PRI)
- Practice instructions
- Service design package packages
- Frequently asked questions
- FAQs,
- User help articles
An output of KM is templates for all these activities, saving significant time and effort for those writing the knowledge, and, most importantly, when staff follows templates, it is easier to store and find with queries. Wait "until the right time," and you will find that many queries don't work. It is a best practice to start with KM guidance as a framework for a knowledge-centered organization.
There is another reason not to wait to do KM. You will notice when looking at the complexity of the SKMS that for KM to work, many different systems must work together. KM must have a hand in choosing IT systems. One of the requirements is that the data must be available to all the other systems. If this does not come naturally, create Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to make it happen.
What is the Known Error Database (KEDB)?
When some people think of Knowledge Management, they think of the KEDB. It is much more than one database. If you look at the SKMS diagram again, you will find KEDB on the far right. The KEDB is a Problem Management root cause analysis database not for the Service Desk.
The architectural layers of SKMS9
The above diagram of the SKMS is the detailed data view. It would be overwhelming if you had to navigate through that every day. Thankfully, KM has a simplified approach that is easier for people to use.
Below is the SKMS four-layers view. This view has a presentation, knowledge processing, information integration, and data layer:
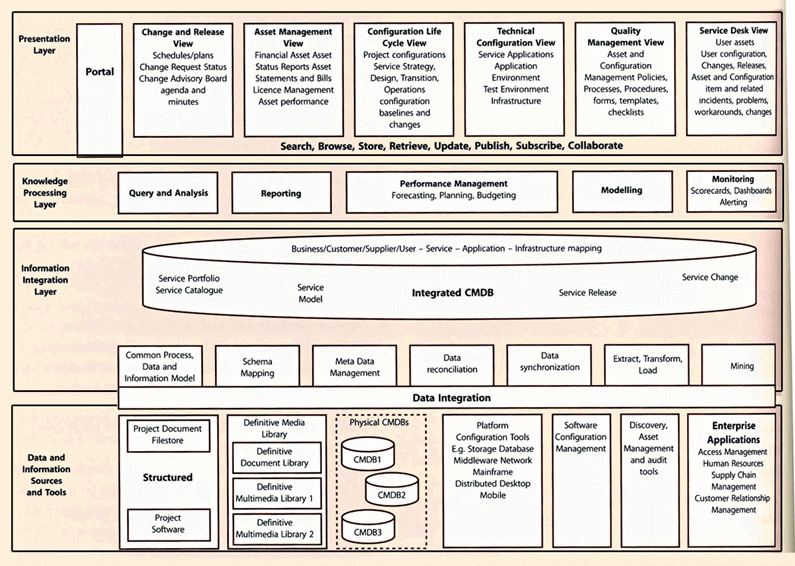
- The tools an organization needs to find, gather, secure, distribute, audit, and archive data are all part of the data layer.
- Tools that allow for the integration of data from many sources are part of the information integration layer.
-
The knowledge processing layer converts the information into valuable knowledge:
- Query and analysis tools
- Reporting tools
- Performance management
- Modelling tools
- Monitoring and alerting tools
-
The presentation layer:
- IT governance view
- Quality management view
- Services view
- Asset view
- Configuration view
- Service Desk and support view
- Self-service view
As you can see, this KM presentation tool makes knowledge easy to use. Users can bring into the query many different databases and create custom reports for reuse.
Critical Success Factors (CSF) and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)10
Critical success factor = A necessary precondition for achieving intended results.
Key performance indicator: A vital metric used to evaluate the success in meeting an objective.
-
CSF: Information and knowledge readily available to assist management decision-making:
- KPI: Greater # of SKMS accesses by management.
- KPI: Higher % of managers' SKMS searches now obtain a "good" rating.
-
CSF: Lowered support and upkeep time and effort requirements:
- KPI: Higher # of times that items like documentation guidelines, test design, and Service Desk scripts have been reused.
- KPI: Reduced # escalations trends and increased resolution at lower staff levels.
- KPI: Increased % of incidents solved by using known errors.
- KPI: Improved outcomes in the service operations teams' KM satisfaction survey.
-
CSF: Early operation of new and modified services with successful implementation and few knowledge-related errors:
- KPI: Reduced # of "knowledge-related" occurrences and issues.
- KPI: Higher % of service transitions that are successful.
-
CSF: Enhanced standards and policy management and accessibility:
- KPI: Higher # of standards and policies kept in the SKMS.
- KPI: Higher # of access times permitted under SKMS standards and procedures.
- KPI: Increased % of standards and policies reviewed by the agreed review date.
- KPI: Increased use of KM templates.
-
CSF: Reduced dependency on personnel for knowledge:
- KPI: Higher # of accesses to the SKMS.
- KPI: Higher % of SKMS searches that users rate as "good."
- KPI: Better ratings for Knowledge Management in normal customer satisfaction surveys.
Roles within the Knowledge Management Practice
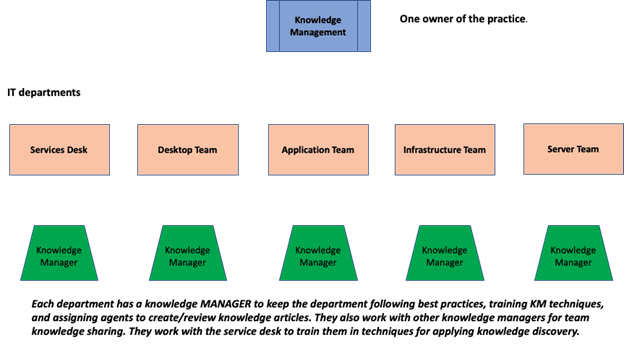
As with all 34 ITIL Practices, one person is the owner and is responsible for the Practice and is responsible for promoting the KM Practice across the enterprise with regular status reports and success stories. Specifically, how KM has brought value to the business.
Supporting the KM Practice are Knowledge Managers within each support team. Their job is to direct the support team in supporting the KM Practice through data quality, knowledge usage, and teamwork with different support teams. KM Managers inform successes to the KM owner and anything else their team is doing with KM.
KM's success is directly related to business leaders' actions11
KM is a culture, a business culture for success. It derives its power from the Continuous Improvement Practice. Learning to create and use KM gives businesses a hedge when turnover happens. No one wants to see critical knowledge walk out the door. No one likes that it takes so long to train new employees. KM is the answer to these realities, but it does not happen without leadership from the top:
- Develop a KM attitude. Sharing knowledge must stop being seen as a duty and start being welcomed. Provide a transparent and creative KM environment where everyone understands the value of their knowledge and its contribution to the organization to foster this mindset.
- Accept the new KM. Today, knowledge is about adding value, and it forms the basis of the remote and hybrid work models that will characterize the workforce after Covid-19. Knowledge transmission, addition, and sharing will all be part of each employee's daily tasks. An organization's knowledge transfer will improve if knowledge transfer is prioritized, and the increased value of information will justify resources being put into in KM repository systems.
- Make good use of sophisticated technologies. AI, visual impact graph technology, and natural language processing provide new interfaces with organizational knowledge. Some add-ons to "regular" knowledge tools include content links, expertise clusters, skill movement, trending themes, on-demand retrieval, and automatic tagging.
Implement KM immediately and start saving money
MetricNet12 published groundbreaking research on the cost of resolving incidents at the different service levels. In the table below, MetricNet demonstrates that it costs the company 314% more if Level 1 must escalate to Level 2 and 573% more to Level 3.
Want to save money with KM? Have Levels 2 and 3 look at all their escalated incidents and ask if the Service Desk could resolve these if they had a helpful knowledge article and, perhaps, some tools and training.
The reason costs go up if not resolved at the Service Desk is the longer time it takes, which means more lost user productivity. Increasing First-Contact Resolution (FCR) also increases Customer Satisfaction (CSAT).
Do you have improvement projects waiting on resources? Sure you do. Completing more projects is another way to save money with KM.
| Support Level | Name | Cost to Resolve Ticket | Total Cost Including Service Desk/Ticket | Percent Increase/Decrease |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Service Desk | $22 | $22 | 0% |
| 2 | Desktop Support | $69 | $69 + $22 = $91 | 314% |
| 3 | IT Support | $104 | $104 + $22 = $126 | 573% |
| Field | Travel to site | $221 | $221 + $22 = $243 | |
| Vendor | Vendor Support | $599 | $599 + $22 = $621 | |
| 0 | Self Help | $2 | -$20 | -91% |
| -1 | Problem Management | 0$ | -$22 | -100% |
| -2 | Search & Destroy (AI) |
Does KM pay for itself? Sure it does. It is the gift that keeps on giving.
Footnotes:
- Forrester, "The modern workplace demands a new approach to knowledge management," March 2022.
- ITIL Foundation, ITIL 4 Edition, Axcelos Global Best Practices, 2018, p. 85
- ITIL 3 Service Transition, Axelos Global Best Practices, 2011, p. 182
- Ibid, ITIL 3, p. 182
- Helpjuice, Knowledge Management Tools
- Ibid, ITIL 3, p. 184
- Ibid, ITIL 3, p. 184
- Ibid, ITIL 3, p. 186
- Ibid, ITIL 3, p. 28
- Ibid, ITIL 3, p. 194
- Deloitte, "The new knowledge management"
- Metrics That Matter - Shift Left, Jeff Rumburg, 8/25/2020

About the Author
Bart Barthold
Bart Barthold is an independent senior ITIL instructor with years of experience in combining ITIL knowledge with practical expertise in running a world-class support organization. He has earned the certificate for the highest level of ITIL training - IT Service Manager, holds an MBA, and he has taught various ITIL certifications and hundreds of students since 2004.
Bart is known for his outstanding performance in IT service management and is a recipient of the Help Desk Institute's prestigious Team Excellence Award in 1998. He also finished second in 1997, making him one of the most decorated IT service managers in the industry.
