IT Asset Management Best Practices: How to Maximize Value, Security, and Compliance
Effective IT Asset Management (ITAM) is the best way to make sure an organization gets the most value from its technology hardware, software, and cloud-based solutions.
IT environments are increasingly complex, making ITAM an integral part of IT Service Management (ITSM) and Information Technology Information Library (ITIL®) practices.
IT Asset Management is about much more than simply managing hardware, software, AI tools, APIs, vendor licenses, and software subscriptions. ITAM requires more than just an inventory list.
ITAM demands a strategic, integrated, and continuously improving approach.
In this article, there's a breakdown of the 8 most useful ITAM best practices. These will help your organization control costs, improve security, and maintain security compliance.

8 IT Asset Management (ITAM) Best Practices
IT service delivery, budgets, and security depend on a successfully managed IT asset inventory.
With these 8 comprehensive best practices — aligned with ITIL 4 principles — organizations can maximize asset value and manage IT assets proactively.
-
Build a Comprehensive and Accurate Inventory
The cornerstone best practice in ITAM is having a complete and accurate inventory of all IT assets. This needs to be a list of hardware and software, including databases, data storage, and things like AI tools and APIs.
This database serves as the single source of truth for all asset-related decisions. It should include multiple layers of information answering the following questions, such as but not limited to:
- Do we own or lease (subscribe to) this asset?
- When did we buy, develop, or subscribe to it?
- What is the expected lifecycle timescale?
- What is its worth (or what does it cost)?
- Who is responsible for upgrades and maintenance?
- If it's a subscription: Who is the vendor, and when do we need to review the contract?
Here's how to compile your comprehensive asset management database:
Use Multiple Discovery Sources
Automated asset identification tools can combine with manual IT asset audits and integrations with other systems. Use ITSM software or procurement platforms to ensure no assets are missed.
It can be easy to miss software because not every SaaS tool in use goes through official procurement channels. That's why manual audits are always essential. Cross-check and verify asset inventory alongside network scanners, agent-based tools, and API integrations.
This multi-layered approach to asset discovery will prevent assets from being overlooked.
Create a Centralized Asset Database
Now that you have this information, consolidate all asset data into a single, centralized database.
This should include everything, such as:
- Hardware specifications
- Software licenses/subscriptions
- Ownership information
- Financials, like SaaS pricing, build costs, depreciation, and flexible use costs
- For example, if it's a cloud-based storage with costs that go up or down depending on usage
- Maintenance records
- License details
Integrate with a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) to maintain consistency across ITSM operations.
Maintain Accurate Asset Records
Update asset records regularly to the current status of each asset, like the location, usage, ownership, and condition.
This makes it easier to support better decision-making. Implement automated workflows that trigger updates when assets are moved, modified, or retired. Make sure these automatic triggers are connected to subscriptions. If one is activated or cancelled, the database remains accurate.
Eliminate "Ghost" Assets
There's always going to be something in the inventory that isn't actually being used. Automated checks can't make up for actual human eyes verifying that an asset exists and is still in use.
Confirm digital inventories with physical checks to remove obsolete, misplaced, or duplicated entries. A distorted asset picture is an inaccurate one. This could impact ITSM budgets if financial planners are still factoring in assets that don't exist anymore.
Regular reconciliation processes help maintain data integrity and prevent budget confusion.
-
Track the Full Asset Lifecycle
Managing the full lifecycle of an IT asset brings efficiency and cost-effectiveness, from procurement to retirement. This aligns directly with ITIL 4's holistic approach to creating ITSM value within every stage of service delivery.
Here is how to track and manage an asset throughout its lifecycle. Remember, software (SaaS), platforms (PaaS), and infrastructure (IaaS) are all assets, even if they're not physical like computers and data centers.
End-to-End Asset Visibility
Track every asset across its lifecycle, which means:
- Purchase (either buying, subscribing, or building in-house)
- Deployment
- Operation
- Support
- Disposal
This 360, end-to-end visibility improves forecasting and helps manage refresh cycles effectively. Implement status tracking that provides real-time insight into asset health and performance.
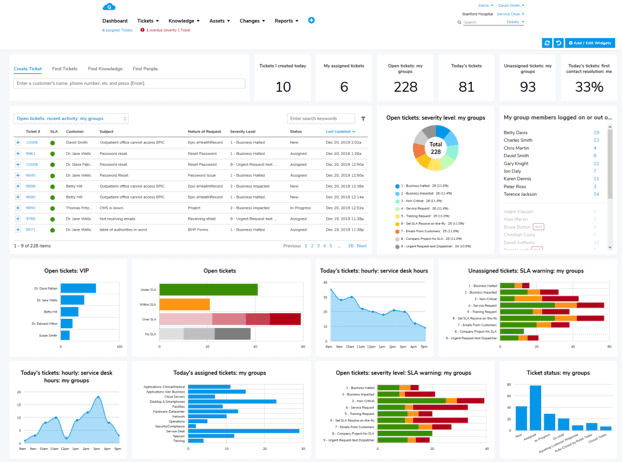
For example, within an ITAM dashboard there should be information about when an update is needed, or when a contract is coming to an end.
Plan for Lifecycle Transitions
Include proactive planning for End-Of-Life (EOL) events, upgrades, and decommissioning. This reduces unplanned downtime and makes sure that IT assets are managed better.
Create automated alerts for software contract expiration dates, lease renewals, and hardware EOL notifications. This could be a chance to move an on-premises solution to the cloud, for example.
Manage Software Subscriptions Proactively
Implement Software License Management (SLM) processes to avoid SaaS bloat.
SLM should also help to maintain license compliance, and improve usage efficiency. Regular license harvesting and reallocation can significantly reduce software costs.
Make sure to include every subscription, to keep track of the real cost of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS being used, and to prevent duplication.
Track Contracts and Renewals
Monitor software and hardware contracts, support agreements, and warranty expiration dates. This helps prevent service interruptions or unbudgeted costs. Integrate with procurement systems to streamline renewal processes.
-
Integrate with AI Tools to Automate Whenever Possible
Efficiency and accuracy in ITAM improve significantly when systems are integrated, and repetitive tasks are automated. AI tools make this even easier, and can be done with most ITAM software.
It also prevents mistakes. We do recommend though doing physical asset checks too, to avoid ghost tech hanging around your budgets and spreadsheets.
Integrate with ITSM Systems and IT Help Desks
Link your ITAM solution to your ITSM platform to enable consistent workflows, better service delivery, and a complete 360 overview. Make sure this is integrated with the following:
- Internal knowledge bases
- External self-serve portals
- FAQs, troubleshooting
- AI agents
- IT Help Desk
These integrations support incident resolution with asset context, and this enables better change management decisions.
Automate Asset Discovery
Real-time discovery tools reduce manual data entry, catch changes instantly, and keep the asset inventory current. Implement continuous monitoring to detect new assets, configuration changes, and unauthorized software installations.
At the same time, check off every automated entry with manual verification, whenever possible.
Automate Routine ITAM Tasks
Automate time-consuming manual tasks such as tagging, inventory updates, license reconciliations, and notifications to reduce the burden on IT teams and improve consistency. Workflow automation helps make sure standard processes are followed and helps reduce human error.
-
Conduct Regular Audits, Focus on Continuous Improvement
A successful ITAM strategy is not static. IT purchasing decisions happen faster than an IT team can track. ITAM requires ongoing validation and refinement, supporting ITIL 4's continual improvement practice.
Run Regular Audits
Schedule internal or external audits to verify data accuracy, highlight potential compliance gaps, and find underutilized or shadow IT assets. Use both scheduled audits and surprise spot-checks to keep data integrity high.
Track Key Performance Indicator Metrics (KPIs)
Use KPIs like the following:
- Asset utilization
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- License/software subscription compliance rate
- Mean time to retirement to evaluate ITAM program effectiveness
Establish benchmarks and track trends to identify improvement opportunities. Integrate these into ITSM and ITIL best practices, and even SLA-based KPIs.
Implement Automatic Feedback Loops
Use audit results, stakeholder input, and data insights to fine-tune how you manage IT assets. Regular review meetings with key stakeholders ensure the ITAM program evolves with organizational, operational, and budgetary needs.
-
Strengthen Security and Compliance
ITAM plays a vital role in strengthening your organization's cybersecurity posture. In turn, this impacts regulatory compliance, and directly supports ITIL 4's risk management principles.
Implement Comprehensive Security Rules
Define and enforce access controls, encryption standards, and acceptable use policies for all IT assets. Your IT assets and data are not secure unless there are robust rules for each asset, so that only the right team members have access to what they need. This also better maintains compliance, especially in regulated sectors.
Implement role-based access controls and regular security assessments to maintain asset security throughout the lifecycle.
Meet Regulatory Requirements
Keep your ITAM practices aligned with compliance frameworks relevant to your industry, such as but not limited to the following:
- ISO/IEC 19770
- GDPR
- SOX
- HIPAA
This is critical when working with vendors, because even if they fail compliance, it could impact your organization, and your security posture. Regular compliance reporting and audit trails demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements.
Protect Asset Data
Secure all data related to every ITAM solution, including configurations, license keys, and location data.
With robust controls to prevent unauthorized access or loss, this is vital in this era of AI deepfakes, and more sophisticated cyberattacks. Implement data classification and protection measures appropriate to asset criticality.
-
Align People with Processes
ITAM programs only succeed with buy-in and training for the right people, with clear ownership, and well-defined processes.
Establish a Dedicated ITAM Function
Whether a small team or a full department, clear leadership and ownership brings accountability. Define roles and responsibilities clearly, including asset custodians, data owners, and process managers.
Define and Document Asset Policies
Standardize processes for asset acquisition, deployment, tracking, maintenance, and disposal with clearly written and enforced policies. Regular policy reviews keep procedures relevant and effective.
Promote Cross-Team Collaboration
Coordinate between IT, finance, procurement, and operations to maintain transparency and data consistency across teams. Regular cross-functional meetings and shared KPIs promote collaboration.
Train Staff and Stakeholders
Provide ongoing training and support to everyone involved in the asset lifecycle to maintain compliance with policies and reduce mistakes. Implement role-specific training programs and regular refresher sessions.
Training is even more important when new hardware or software is introduced. Make sure everyone knows how to use anything new being integrated into your existing IT systems.
-
Implement Strategic Financial Management
Effective ITAM requires sophisticated financial management that goes beyond basic cost tracking to support strategic business decisions.
Establish Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Models
Develop comprehensive TCO models that include acquisition costs, operational expenses, maintenance, support, and disposal costs. This approach enables better investment decisions and budget planning.
It's also why ITSM leaders need the complete picture of every IT asset being used, to budget accurately.
Implement Automated Asset Depreciation Tracking
Track asset depreciation according to your organization's accounting standards. Make sure they're in-line with business policies. Accurate depreciation models support financial reporting and help identify optimal refresh cycles.
Conduct Regular Cost Optimization Reviews
Regularly analyze asset utilization and costs to identify optimization opportunities. This includes license harvesting, hardware consolidation, and renegotiating vendor contracts based on actual usage patterns.
-
Optimize Service Delivery with ITAM Integration
Align ITAM practices with ITIL 4 and ITSM best practices to enhance service delivery and customer satisfaction.
Support Incident and Problem Management
Have asset information readily available to support teams during incident resolution. Rich asset data including configuration details, warranty status, and maintenance history accelerates problem diagnosis and resolution.
Enable ITIL-Empowered Change Management
Provide change management processes with accurate asset dependency information and impact analysis capabilities. Understanding asset relationships and configurations supports better change planning and risk assessment.
Support Capacity and Availability Management
Provide capacity planning teams with accurate asset utilization data and performance metrics. This information supports infrastructure planning and helps prevent service degradation due to capacity constraints.
Let's now look at how ITAM and ITIL connect and interact with one another, and then we've provided more useful information with FAQs.
ITIL 4 and ITAM Combined to Improve Service Value
IT Asset Management in ITIL 4 is not a standalone practice but an integral part of the service value system. Here's how ITAM connects to key ITIL 4 concepts:
ITAM supports the following value chain activities:
- Plan: Asset data informs strategic planning and investment decisions
- Improve: Asset performance metrics drive continual improvement initiatives (an integral part of ITIL4)
- Engage: Asset information supports customer and stakeholder engagement and buy-in
- Design and Transition: Asset capabilities and constraints shape and modify service design, including continual improvement initiatives
- Obtain or Build: Asset procurement and deployment processes
- Deliver and Support: Asset information supports ITSM service delivery and support ticket resolutions
At the same time, ITAM needs to be integral across all 4 ITIL dimensions:
- Organizations and people: ITAM and ITSM roles, responsibilities, and competencies
- Information and technology: Asset data, discovery tools, inventory management, and ITAM platforms
- Partners and suppliers: Vendor management and 360 contract oversight, with budget control
- Value streams and processes: ITAM workflows integrated with ITSM at every stage of service delivery
The following ITIL 4 guiding principles as they apply and interact directly with ITAM:
- Focus on value: Align asset decisions with business outcomes
- Start where you are: Assess current ITAM maturity before transformation
- Progress iteratively: Implement ITAM improvements in manageable stages, according to continual improvement initiatives
- Collaborate and promote visibility: Share asset information across teams (don't silo key asset information)
- Think and work holistically: Consider asset impact on the entire ITSM service ecosystem
- Simple and practical: Whenever you can, avoid over-complicating ITAM processes
- Optimize and automate: Keep using technology, like AI, to improve ITAM efficiency
Careful IT Asset Management Planning Now Brings Less Care Later
Implementing strong IT Asset Management best practices is essential for modern ITSM teams. The goal with this is to stay efficient, secure, and compliant.
With a structured, data-driven approach to ITAM — supported by integration, automation, and collaboration — organizations can reduce risk, lower costs, and make smarter IT asset purchasing, building, and buying decisions.
When integrated with ITIL 4 practices, ITAM becomes a strategic enabler that supports the entire service value system. From incident resolution to strategic planning, accurate and comprehensive asset information drives better decisions, and improved outcomes.
Whether you're optimizing a mature ITAM program or building one from scratch, these best practices serve as a reliable foundation for success.
Remember that ITAM is not just about tracking assets — it's about enabling business value through intelligent asset optimization and management.
Useful IT Asset Management Resources
- IT Asset Management (ITAM) in the Cloud
- Get helpful ITIL resources with insights from our industry experts and best practices
- AI-Powered Knowledge Article and Ticket Copilots
- Tough Questions to Better Select, Compare and Evaluate Any Software or Cloud Vendors
Giva's IT Asset Management is Seamlessly Integrated with Our Full-Function ITSM Software
Let Giva be your partner for all of your IT Service Management needs, including our seamlessly-integrated and ITIL®-aligned IT Asset Management application with Software Management:
- Gain total visibility into your IT assets — no more guesswork
- Speed up compliance and audits with centralized asset data
- Reduce manual effort with easy asset management workflows
- Make smarter IT decisions with actionable asset reporting
- Help safeguard hardware and software with little effort
Get a demo to see Giva's solutions in action, or start your own free, 30-day trial today!
IT Asset Management (ITAM) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What are the 5 P's of Asset Management?
The 5 P's of asset management are a strategic framework used to guide effective asset management:
- People: Individuals and teams responsible for managing and maintaining assets, including their skills, training, and where they sit in an organizational structure.
- Processes: Workflows, policies, and procedures governing how assets are handled throughout their lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal. In many ways, the processes are the most important part of all of this. If you have solid processes in place, then everything else is organized accordingly.
- Products: Tools, software, and other tech used in asset management, including discovery tools, CMDB systems, and ITAM reporting platforms. All of this needs to be integrated with ITSM, change management, and IT support ticket software. Nothing about ITAM should sit in isolation.
- Partners: External vendors, service providers, and stakeholders involved in IT asset and software procurement, support, and management activities.
- Performance: Various metrics and KPIs used to evaluate asset utilization, cost-efficiency, compliance, and ITSM program effectiveness. All of which is influenced by ITAM, in the same way that ITAM impacts ITSM and ITIL.
These 5 elements help align asset management with organizational goals, and ensure sustainable program success.
-
What are the 4 pillars of Asset Management?
The 4 pillars of asset management provide a structure for building a reliable and sustainable ITAM strategy:
- Governance: Establishing clear ownership, accountability, compliance standards, and decision-making frameworks that align with business objectives.
- Lifecycle management: Managing assets comprehensively from acquisition through to disposal, including planning, deployment, maintenance, and retirement.
- Information management: Maintaining accurate, complete, accessible, and timely asset data that supports informed decision-making across the organization.
- Risk management: Identifying and mitigating risks related to asset loss, non-compliance, security vulnerabilities, and business continuity threats.
Combined, these 4 pillars support informed decision-making, value optimization, and sustainable asset management practices across an IT team, or several teams.
-
What is Asset Management in ITIL 4?
In ITIL 4, ITAM supports the overall service value system. It involves the planning and management of the full lifecycle of all IT assets to:
- Maximize value realization from asset investments
- Control and optimize costs throughout the asset lifecycle
- Manage risks related to compliance, security, and business continuity
- Support informed decision-making about purchases, reuse, and disposal
- Keep regulatory and contractual compliance
- Enable effective service delivery and customer satisfaction
ITAM in ITIL 4 is closely integrated with other practices like Configuration Management, Change Enablement, Financial Management, and Supplier Management, creating a holistic approach to IT service management.
-
What is the IT Asset Management lifecycle?
The IT asset management lifecycle refers to the end-to-end stages an IT asset goes through during its time within an organization:
- Procurement: Acquiring the asset through purchase, leasing, or other acquisition methods, including vendor selection and contract negotiation.
- Deployment: Installing, configuring, and implementing the asset for productive use, including user training and initial support setup.
- Usage and operation: Day-to-day utilization and support, including performance monitoring, user support, and ongoing optimization.
- Maintenance: Ongoing updates, repairs, performance monitoring, and lifecycle management activities to offer continued value delivery.
- Retirement and disposal: Secure decommissioning, data sanitization, and disposal or recycling according to security and environmental policies. This stage needs to be done well with hardware to make sure an asset is either getting recycled, or disposed of without doing further environmental damage.
Effectively managing this lifecycle keeps assets optimized for maximum value, risks are minimized, and costs are controlled. All of this also makes sure that compliance requirements are met throughout an IT asset's useful lifecycle.