Our Big List of As-A-Service Acronyms
The cloud is so much more than new-era data storage. It has grown to offer services of all kinds to businesses, healthcare organizations, educational faculties, and more. You may already be familiar with "Software as a Service" or the SaaS meaning. While that is a well-known expansion of cloud as a service, there are many other acronyms you may be unaware of. Each acronym reflects another capable service of the cloud — one or more of which may be of value to you and your organization. Continue reading as we have created a master listing of each service related to today's cloud technology.

Anything as a Service (XaaS)
What is XaaS? As the title suggests, it stands for "anything as a service." This acronym is a great place to start because it is the most encompassing of the bunch. It is a general category of services related to the cloud. It can be any product, tool, or service delivered to an end-user via the internet. In this model, organizations look to pass IT responsibility off to a service provider, who then monitors and manages the service as part of a contract. XaaS is attractive because it is highly customizable. An organization only purchases services they need and can scale up or down depending on demand. In addition to cost savings, your business also saves time, as employees, specifically those in charge of IT, can focus on other tasks knowing that these services are being professionally managed.
Cloud as a Service (CaaS)
Cloud as a Service, or CaaS, is an umbrella term used to describe several niche cloud computing solutions over the internet. These can include services like, IaaS, PaaS and SaaS — services which we will speak more about in this piece.
AI as a Service (AIaaS)
Artificial intelligence (AI) is designed to mimic human capabilities to conduct tasks. Whether it be online chats for customer service or data entry and calculation for sales teams. Unfortunately, many small to medium-sized organizations would be "priced out" of developing this technology themselves. Factors contributing to these difficulties include the size of machinery, a short supply of programmers, and above all, time and financial constraints — especially when you are running an organization simultaneously. With AI as a Service (AIaaS), organizations can implement this advanced technology without the burden of in-house development. It can be used for several purposes including, customer service (live chat bots), data entry and analysis, automatic production, and more. The reasoning, learning, and thinking capabilities of AIaaS can free up time for your staff while providing a more seamless experience for your clients.
AIaaS Examples/Providers:
- MonkeyLearn
- Google Cloud AI
- IBM Watson
- Amazon AI
Backend as a Service (BaaS)
The backend for a mobile app or web program can sometimes prove to be the most complicated. Since it is not "forward facing", it is usually home to the most complex tasks of a machine. With that in mind, it is also likely to be the area that requires the most hands-on attention from IT teams, whether it be maintenance, repairs or data mining and forwarding. Backend as a Service, or BaaS for short, is the process of outsourcing the maintenance and control of this part of the service to a third-party organization. Your internal teams will still manage the frontend of the application. BaaS will usually involve some or all of the following areas of tech:
- Hosting
- Cloud storage
- Push notifications
- User authentication
- Database management
BaaS Examples/Providers:
- 8Base
- Apache Usergrid
- AWS Amplify
- Back4App
Backup as a Service (BaaS)
Backing up data is one of the most important steps you can take when it comes to organizational security. If you encounter a cyberattack or device theft, being able to wipe or restore data remotely is key in ensuring the limitation of downtime and reducing the impacts of stolen personal information. Data backups are easy to conduct and can often even be automated. Despite this, it is sometimes equally as easy to forget to do it regularly. When you outsource data storage to a cloud service provider, they may offer regular data backups as part of their service offering. Backup as a Service (BaaS), ensures a recent copy of your data is available in the most unexpected moments. The frequency of backups will depend on data sensitivity, the risk associated with cyber criminals and your organization, and the amount of new information created. Generally speaking, backups should occur 2-3 times per week at most organizations.
Backup as a Service Examples/Providers:
- NinjaOne Backup
- Vembu Cloud BDR Suite
- Acronic Cyber Protect
Blockchain as a Service (also BaaS)
As described by Deloitte, blockchain is a, "shared, immutable record of peer-to-peer transactions built from linked transaction blocks and stored in a digital ledger. Blockchain relies on established cryptographic techniques to allow each participant in a network to interact (e.g. store, exchange, and view information), without preexisting trust between the parties."
As is the case with some of the other services already discussed, building and managing your own blockchain can be difficult and expensive — especially if you're a small or medium-sized organization. Blockchain as a Service, or BaaS for short, allows an organization to access an existing blockchain network. These services can be managed online or on mobile applications and are highly configurable.
Blockchain as a Service Examples/Providers:
- IBM Blockchain Platform
- Oracle Blockchain Cloud
- Azure Blockchain Service
- Alchemy
Content as a Service (also CaaS)
Content is everywhere. Read the news on your smartwatch or check the weather on your fridge — almost all technological items offer the end user content these days. Providing content to different platforms can be time-consuming and expensive for an organization. For example, the way content is formatted for an Apple Watch can be different from how it is formatted for a Samsung Galaxy Tablet. If an organization does not have the resources to format content for many platforms, its reach will become severely limited. With Content as a Service, or CaaS, an organization can upload raw data, and the service provider will format it to work in many available places. The appropriate example of Spotify is shared by CONTENTSTACK who note that "the popular music platform lets artists upload their music, then Spotify takes care of the formatting and delivery. Listeners can listen to the same song in their car, on their iPhone, or via Google Home."
CaaS Examples/Providers:
- MediaShower
- Contentful
- BloomReach
- CONTENTSTACK
Data as a Service (DaaS)
With the onset of so much new technology, organizations can ingest massive amounts of data. More data can seem like a valuable resource, but it serves little purpose if you cannot analyze it. This roadblock can be due to the complexity of the data, staffing resources, or other related reasons. Data as a Service (DaaS) can help an organization with storage, management, and analysis. It can be especially helpful in provisioning data coming from several different sources. For healthcare organizations, this service can help to maintain data integrity, while for a business, it can help to forecast consumer trends and promote more efficient decision making.
DaaS Examples/Providers:
- Urban Mapping
- Xignite
- D&B Hoovers
Data Management as a Service (DMaaS)
Data Management as a Service (DMaaS) is a sibling of Data as a Service (DaaS). This service refers to the centralized storage of data on behalf of an organization. Although the main service is storage, it could provide other services like backups, restores, and mobile access.
Examples of storage providers that also offer DMaaS services:
- Oracle
- IBM
- SAP
- Microsoft Azure
Examples of Data Management Software tools:
- SAP Master Data Governance Tool
- Ataccama
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)
As electrical grids become increasingly overwhelmed, and the world's environment continues to change, it is not unlikely that we see more "disasters." We apologize for being so bleak, though natural disasters, like tropical storms, are becoming more prevalent, as are rolling power outages. Both scenarios can wreak havoc on organizations of all types. It can knock systems offline, resulting in permanent loss of data and damage to infrastructure. This is especially true if data is held on-site and not backed up to an external drive or network. When you deploy Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS), an external organization will physically or virtually host your servers in either one or more secure locations across the globe. When disaster strikes, this option allows the third party to apply a helpful hand in data and infrastructure recovery and preservation. You might be wondering what the difference is between DRaaS and Backup as a Service (BaaS). To clarify, BaaS solely backs up data, while DRaaS backs up data and infrastructure. Infrastructure can be expensive to replace, so if you live in an area prone to natural disasters, going the extra mile with the protection offered by DRaaS may be worth it.
DRaaS Examples/Providers:
- Microsoft Azure Site Recovery
- Quorum onQ
- Zerto Virtual Replication
- Zetta Backup and Recovery
Encryption as a Service (EaaS)
According to information shared in the Cost of a Data Breach Report by IBM, "The global average cost of a data breach in 2023 was USD 4.45 million, a 15% increase over 3 years." Encryption as a Service, or EaaS for short can help to disrupt these types of attacks on your organization. A service available in the cloud, EaaS encrypts data in all stages — at rest or in-transit. The feature scrambles data, like passwords, to ensure they are safe even when traveling over wide area networks (WANs) — a major point in susceptibility.
EaaS Examples/Providers:
- CloudHesive
- FortKnoxster
- HashiCorp Vault
- Identos
Hardware as a Service (HaaS)
Depending on financial situations, it may not make sense for an organization to purchase the hardware outright. Hardware can include items like, but not limited to, physical servers, warehouse inventory scanners, and mobile devices like smartphones. The Hardware as a Service model (HaaS) refers to a third-party leasing equipment to an organization. The benefit of this model is that organizations do not need to pay hefty upfront fees or maintain devices (for example, software updates and warranty replacements). Often, an organization is also receiving new in-market tech. These devices are returned after some time and can be refreshed with something more advanced. Organizations should ensure that this model makes sense for them by calculating the lease cost over time, in comparison to an outright purchase price.
HaaS Examples/Providers:
- Geek Force USA
- Hexis Consulting (HaaS Services)
- Xyte
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
What is IaaS?
If you are looking to define IaaS, or Infrastructure as a Service in cloud computing, then you will want to know that it serves the purpose of offering virtual services online. Depending on your needs, IaaS can be scaled up or down with ease. It eliminates the need to purchase physical infrastructure and provides services like storage and security to an end user or organization.
IaaS Examples/Providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud
- DigitalOcean
Read more: Three Main Categories of Cloud Computing: IaaS, PaaS and SaaS
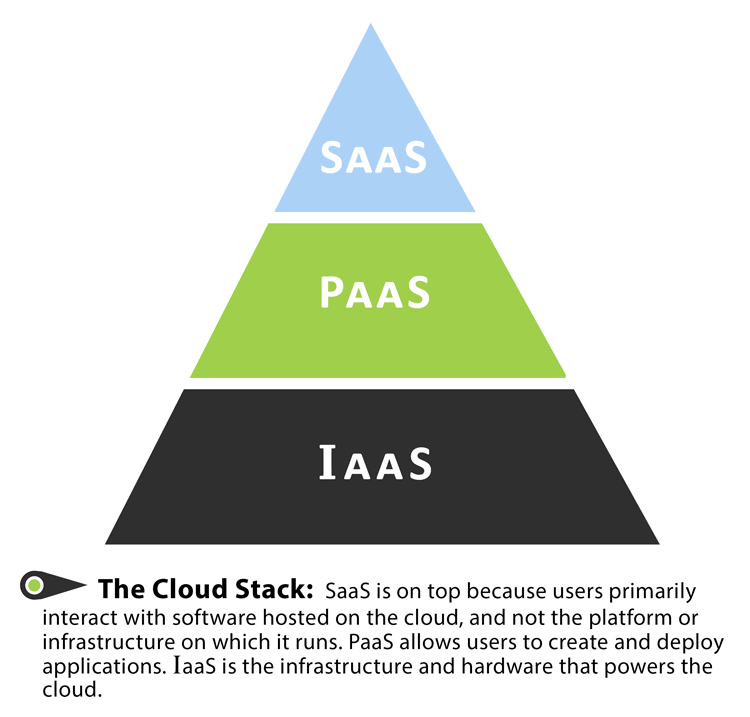
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
What is PaaS, or Platform as a Service? Think of it as a sandbox for development. The sandbox can accommodate the resources required to build out applications based in the cloud. An organization can purchase these resources on a pay-as-you-go model. PaaS is the total package. It includes all of the infrastructure from servers through to storage. Whether it be building or testing a new web application or managing something that already exists, Platform as a Service is your one-stop-shop for all things related to applications in the cloud. The main benefit for organizations will be savings realized by not having to buy or manage software licenses.
PaaS Examples/Providers:
- Amazon Web Services
- Microsoft Azure
IaaS vs PaaS — What's the Difference?
In the simplest of terms, the difference between Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) is internal and external. To be more specific, IaaS allows an organization to manage business resources in the cloud — think servers and storage, while PaaS allows an organization to host, build and deploy forward-facing applications. They are closely intertwined, as one cannot happen without the other.
Integration Platform as a Service (IPaaS)
The cloud can be an overwhelming concept. This is especially true when factoring in connected applications and how they integrate and communicate together. As you can imagine, it can turn into a complicated web of dysfunction. Integration Platform as a Service (IPaaS) aims to simplify the development of integration flows related to connected applications. This process is all done without the need to install or manage hardware. Managing this at the organizational level can be time-consuming and confusing. Allowing a third party to manage this for you is an easy solution. Ultimately, they will ensure that any connected applications you choose for your cloud setup work together and offer automation.
IPaaS Examples/Providers:
- Workato
- Dell Boomi
- Oracle Integration Cloud
- TIBCO Cloud
Information Technology as a Service (ITaaS)
Not all organizations have in-house IT teams. For small and medium-sized businesses, there may be little purpose to having a full or part-time IT person on the payroll. Besides financials, there may not be enough tech (or complex tech issues) to have IT on the direct staff. It might make sense to utilize IT as a Service (ITaaS). Unlike many other definitions visited throughout this piece, this one does not directly deal with the cloud. With ITaaS, some or all IT functions are contracted out to a service provider. For example, if an employee notices an issue with laptop performance, they can email a ticket to the IT service provider. The service provider will manage the issue with a physical visit, a call, or a virtual screen takeover.
ITaaS Examples/Providers:
- CyberDuo
- Field Nation
Knowledge as a Service (KaaS)
Knowledge as a Service (KaaS) goes beyond providing data — it provides a user with data AND context. How does this type of service achieve these results? KaaS is built on a knowledge model that draws on other models like neural networks and decision trees to come to a conclusion. Users input a request, and the service provider runs that through a "centralized knowledge server." Building on the concept of Data as a Service (DaaS), KaaS digs deeper into the relevance of requested data. KaaS can provide items like definitions and data associations with added context. This service can also help to build trust between humans and machines as there becomes a rationale for the information being shared.
KaaS Examples/Providers:
- Bloomfire
- Serviceware SE
- Support Hero
Mobile Backend as a Service (MBaaS)
Web and mobile applications are meant to be seamless for the end user, though what goes on in the back end is anything but simple. Developers must link their application from front to back into the cloud and other Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). These connections ultimately drive user features like push notifications and social media integration. Since each feature requires an API, the process can be time-consuming and complex for in-house developers. To keep a project moving, an organization can opt to have in-house developers work on the front-end while leaving the more complex task to a Mobile Backend as a Service (MBaaS) provider.
MBaaS Examples/Providers:
- Back4App
- Parse
- Firebase
Monitoring as a Service (MaaS)
Falling under the category of Anything as a Service (XaaS), Monitoring as a Service (MaaS) is the function of tracking certain cloud applications, networks, and systems in their live state. This tracking usually involves ensuring that systems are operating without disruption.
MaaS Examples/Providers:
- Altnix
- Paessler (PRTG Hosted Monitor)
- Datadog
Network as a Service (NaaS)
Network as a Service, or NaaS for short, is a solution that provides entire network rentals to a client. These cloud-based networks allow for an organization to conduct complete customization without the hassle of maintaining infrastructure themselves. NaaS can be a cost-effective alternative to corporate tech needs in areas like:
- Virtual private network (VPN)
- Multiprotocol Label Switching Connections (MPLS)
- Firewalls
- Load balancers
NaaS Examples/Providers:
- Perimeter 81
- Aryaka SmartServices
- Cisco Plus NaaS
Operations as a Service (OaaS)
Operations as a Service (OaaS) is there to assist organizations with deployment and overall management of in-house systems. These can be cloud systems or other legacy infrastructure. Although your on-site IT team can do some work to keep the production environment online and up to date, outsourcing some aspects of maintenance can be good practice. This ensures certain (sometimes tedious) tasks are completed on a regular basis — this can include:
- Implementing security patches for applications and operating systems
- Downtime support
- Efficiency recommendations — to help you scale services and save money
- Creating staging and testing environments as needed
- Coordinating system backups
OaaS Examples/Providers:
- World Data Products
Software as a Service (SaaS)
What does SaaS stand for?
Software as a Service, of course! There's a very good chance that you have heard of this term before — it is certainly one of the most popular "as a service" models in the market. The concept itself is also quite straightforward.
SaaS Definition
SaaS in cloud computing is the practice of licensing and delivering software to an organization. The software is centrally hosted, and the recipient pays a subscription fee on a time-based interval for the service.This "on-demand" software service is often web based. A popular example of a SaaS product is Dropbox — the file storage platform used across many industries.
Giva also provides a suite of SaaS products, including Customer Service, IT Help Desk, Asset Management, Knowledge Management, IT Change Management and Service Desk. Why not sign up for a free trial today?
Video as a Service (VaaS)
Video as a Service, or VaaS can play a critical role in modern day businesses. It is a service where point-to-point video conferencing software is provided to an organization over the internet. During the COVID-19 pandemic, many organizations realized the value in online collaboration tools. Fast-forward to today's post-pandemic workforce, and many of these tools continue to be used. They have reduced the need for business travel and face-to-face meetings. This is especially true of VaaS services which bridge the gap between virtual connections and reality. One of the most popular VaaS services is Zoom, the video conferencing software used for 1-on-1 chats and full-blown conferences with thousands of attendees!
VaaS Examples/Providers:
- Zoom
- GoToMeeting
- TeamViewer
Workspace as a Service (WaaS)
Whether you are a brand new organization looking to set up an office space, or an existing organization looking to overhaul corporate tools, determining which tech to use in each segment of your operation can be overwhelming. That is where Workspace as a Service, or WaaS for short, can come in handy. This service can provide several tech packages to organizations to get them up and running for their suppliers and clients alike. Although you would not need to purchase everything offered, a WaaS offering can include features like:
- High-speed internet access
- WAN Networking
- Communications (telephone and other cloud-based communication methods)
When you are not sure where to start with enterprise-level tech, looking into a WaaS package can get you covered without all of the stress of wondering if you are missing something.
WaaS Examples/Providers:
- Ace Cloud Hosting
- V2 Cloud