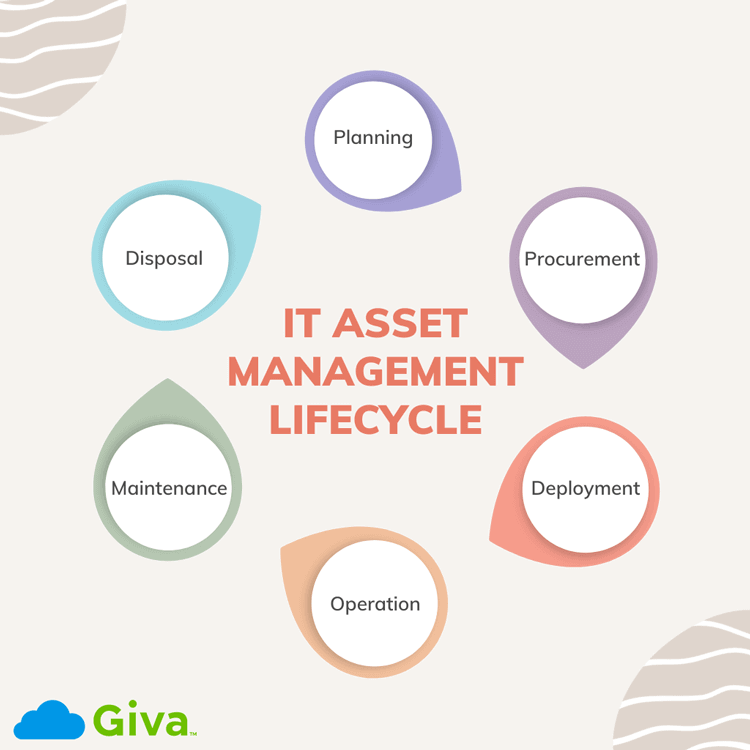
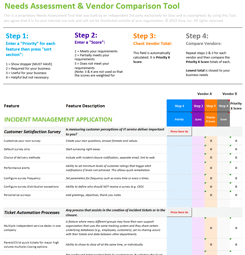
What is Demand Management and How Does it Work in IT?
As the pace of innovation accelerates, companies must keep up with the latest trends to remain competitive. This, in turn, places a significant burden on the IT department to manage and maintain the technological infrastructure and to identify and implement new technologies. As a result, IT professionals are under mounting pressure to deliver high-quality services in a timely and cost-effective manner, all while ensuring the security and reliability of critical systems.
In this blog post, we'll explore the concept of Demand Management within IT, including the process, roles and responsibilities involved, and benefits for implementing Demand Management in your organization.

Examples of Demand Management Outside of IT
But first, let's review Demand Management in more commonly-understood ways.
The term "Demand Management" is used across a spectrum of industries outside of IT. A few notable Demand Management examples include:
- Retail: Forecasting customer demand for specific products and services and aligning inventory and supply chain operations accordingly. This process helps retailers optimize their inventory levels and reduce waste. It also ensures products are always available for customers, which improves customer satisfaction.
- Energy: The process of balancing energy supply and demand in real time. Technologies such as smart grids, sensors, and analytics monitor and adjust energy usage based on changing demand patterns.
- Healthcare: Optimizing healthcare resources such as hospital beds, staff, and medical supplies based on patient demand. Doing this helps healthcare organizations reduce costs, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the overall quality of care.
-
Cloud computing: Demand Management in cloud computing involves monitoring resource utilization, predicting future demand, and scaling resources up or down as needed to ensure that the provider can meet the needs of their customers.
For example, a cloud service provider may learn to anticipate increased demand for services during peak usage periods. They can then automatically scale up their infrastructure to meet that demand. This helps to improve service availability and reliability.
What Is Demand Management in IT?
At its core, Demand Management is concerned with forecasting, understanding, and fulfilling the IT needs of an organization. IT services can then be delivered efficiently while enabling informed decisions about allocating IT resources. Further, this will help align IT resources with business goals and priorities.
Demand Management is an important component of IT Service Management, particularly within the framework of ITIL® (Information Technology Infrastructure Library).
Benefits of IT Demand Management
IT Demand Management benefits organizations by helping them better manage services to meet the needs of the business and their customers. This can be whether you are a service provider or recipient:
- Better resource utilization: By forecasting and managing demand, IT organizations can improve resource utilization and reduce waste.
- Increased efficiency: By managing demand, IT organizations can reduce the need for reactive and unplanned work, allowing them to focus on proactive work. Think about running out of cloud storage space — IT departments should rarely find themselves in this situation!
- Improved financial management: Demand Management helps organizations understand the cost of IT services. This allows them to manage their budgets and investments more effectively. Whether providing or receiving, IT teams should know what their product is worth or how much needs to be ordered to be fiscally responsible yet functionally efficient.
- Improved service levels: Demand Management helps IT organizations better understand the demand for their services. This then allows them to ensure that service levels are appropriate and meet customer needs.
Good to know — Change Management vs. Demand Management: Change Management focuses on controlling and managing changes to IT services and infrastructure, while Demand Management focuses on forecasting and managing demand for IT services to meet business needs. Learn more: ITIL Change Enablement Framework
How Does Demand Management Work?
Are you interested in getting a more efficient Demand Management structure in place at your workplace? Getting started can be daunting. Follow these steps towards a more streamlined Demand Management process (with a side of emphasis on the importance of Demand Management in supply chain planning):
- Forecast demand: The first step in Demand Management is to gauge demand for the product or service. This process can happen through historical sales data, market research, and other relevant data sources. For example, an organization may analyze past sales trends and use that data to project future demand.
- Analyze demand patterns: Once demand has been forecast, the next step is to analyze demand patterns. This process involves identifying the factors that affect demand, such as seasonality, customer behavior, and market trends. For example, an organization may analyze customer behavior and identify the times of the year when demand is highest.
- Plan production/purchasing: Through the demand forecast and demand patterns, the company can then plan for purchasing or based on production capacity. This process involves determining the optimal production level to meet the expected demand while minimizing excess inventory. For example, an organization may adjust its production schedule to align with periods of high demand.
- Adjust pricing: Pricing is a critical part of Demand Management. By adjusting prices, the company can influence demand and increase revenue. For example, an organization may offer discounts or promotions during slow periods to stimulate demand.
- Monitor and adjust: Demand Management is an ongoing process that requires constant monitoring and adjustment. The organization must track demand and adjust production, pricing, and marketing strategies.
The Bottom Line: IT Demand Management is a Never-Ending Process
In today's fast-paced world, technology advances at an unprecedented rate while customer demands evolve in tandem. This dynamic creates a challenging and perpetual job for IT professionals. The task of keeping up with changing patterns and trends can become overwhelming for IT teams, particularly when they are already responsible for ensuring the security and reliability of critical systems.
However, implementing a Demand Management process, as described earlier, can help your organization stay competitive by leveraging the latest technologies and keeping your customers satisfied with a wide range of products.