16 Challenges in IT for 2025 and What Teams Can Do to OvercomeThem
In 2025, IT Service Management teams are facing more challenges than ever. In this article, we review the top 16 challenges in IT that many leaders and CIOs are saying they're struggling with. We also suggest what can be done to resolve these issues.
From increased cybersecurity threats, especially with the use of "deepfake" AI-based technology, to budgetary constraints, recruitment and retention challenges, to managing data security, working in IT involves constantly juggling new (and old) challenges.
Let's examine some of the most relevant, recurring, and new IT challenges for 2025.
Top 16 Challenges in IT in 2025
-
Growing Cybersecurity Threats (Including AI-Based Dangers)
Cybersecurity threats have always been front-of-mind with IT leaders. This is even in organizations with dedicated cybersecurity managers. However, ITSM team members and leaders need to be hyper-vigilant over the use of "deepfake" AI-based technology in the hands of cybercriminals.
That's right, in 2025, IT leaders are battling all of the usual cybersecurity threats, and AI is increasingly being used to create "deepfake" videos that are costing companies millions in fraud. In fact, deepfake threats are sharply increasing and could generate fraud losses up to $40 billion per year in the U.S. by 2027.
Deepfake videos are as much a training issue as an IT one. In most cases, a deepfake is only going to work if emails appear to genuinely come from a colleague, usually a senior leader, or a verified supplier.
What You Can Do
- Deploy Deepfake Detection Tools: Install AI-based detection software to scan emails, video meetings, and incoming media for fakes.
- Require Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Everywhere: Make MFA mandatory for all sensitive approvals, communications, and financial transactions.
- Train Employees to Spot Deepfakes: Run awareness training highlighting deepfake red flags (weird blinking, voice oddities, unnatural movement).
- Update Incident Response Playbooks: Add specific steps for handling deepfake threats, including verification protocols and escalation paths.
- Monitor for Impersonation Threats: Continuously scan social media, internal networks, and the dark web for signs of impersonation or fake media targeting your organization.
-
Cloud or On-Site Storage
A more traditional concern is managing cloud or on-site storage. Companies need to decide whether they should bring data storage and management back in-house and on-site.
In recent years, there's been a growing concern in IT and from CIOs that too much of an organization's infrastructure is outsourced in data centers.
One SaaS leading the revolution back to on-site, whereby companies control their own infrastructure and software, is 37Signals. Realizing that not every CIO wants to manage 5 or 6 figures in SaaS spend every month, 37Signals has created ONCE. We expect this trend could accelerate in 2025.
What You Can Do
Here are several key questions to consider in order to determine the best next steps for your organization:
- Security and Compliance: Do you need greater control over sensitive data to meet strict compliance, security, or confidentiality requirements?
- Cost Comparison: Will owning and managing your infrastructure save more over time compared to ongoing cloud fees and hidden costs?
- Performance Needs: Do you require ultra-low latency, real-time processing, or bandwidth that local hosting could better support?
- Staffing and Support Capabilities: Do you have (or can you build) the in-house expertise and resources to manage secure, always-on infrastructure with full backup and recovery?
- Scalability and Growth Patterns: Are your data needs stable enough to justify in-house storage, or do they fluctuate in ways that cloud scalability better supports?
- Resilience and Downtime Risk: Can you reliably handle outages, backups, and disaster recovery on-site without increasing risk?
- Strategic Control and Investment Approach: Would owning your infrastructure reduce vendor lock-in, offer a competitive advantage, and align with your ability to make upfront investments?
- Business Fit and Long-Term Vision: Does in-house data management support your company's long-term strategy better than the flexibility of cloud solutions?
-
IT Skills Gap and Recruitment
IT is a challenging sector for recruiting and retaining talent. Not only that, but it is predicted by IDC that 90% of global organizations will be affected by the lack of IT skills among IT professionals by 2026. This will potentially culminate with $5.5 Trillion in losses caused by all of the peripheral effects.
Organizations need to assess where there are skills gaps within IT teams. They should also review how extra training and other support can be provided to help improve team member productivity.
What You Can Do
Consider the following items to determine the status of your organization's IT skills gap and what is needed to narrow and eliminate it:
- Identify Needed Skills: Define what skills are needed now and in the near future based on your IT roadmap.
- Inventory Current Skills: List each team member's current skills, certifications, and tool experience by role.
- Use Self and Manager Assessments: Ask employees to rate their skills, and get manager input to validate accuracy.
- Analyze Work Performance: Review tickets, project outcomes, and delays to spot where skills may be lacking.
- Use Skills Assessment Tools: Leverage platforms like Pluralsight or LinkedIn Learning to evaluate skill levels objectively.
- Benchmark Against Industry Standards: Compare your team's capabilities to common frameworks or competitor standards.
- Prioritize Critical Gaps: Focus on gaps that could delay projects, increase security risk, or reduce service quality.
- Build Learning Plans: Create individual growth plans using training, mentoring, or hands-on experience.
-
Budgetary Constraints
IT leaders with budgets to manage are constantly worrying about whether they're spending them the right way and if they'll be renewed for the next fiscal year. CIOs have a lot to juggle: staff, vendors, storage, SaaS providers, and cybersecurity.
What You Can Do
To keep budgets relevant and defensible, consider the following action points:
- Connect Spending to Business Goals: Show how IT investments support growth, efficiency, security, or customer satisfaction.
- Track and Share Results: Use KPIs to prove impact and regularly update leadership on performance.
- Reallocate When Needed: Shift funds from low-value areas to higher priorities to stay aligned and efficient.
- Stay in Sync with Business Needs: Collaborate with other departments to keep IT aligned with evolving goals.
- Communicate Risks of Underfunding: Clearly explain what's at stake if critical areas like cybersecurity or uptime are cut.
- Speak the Language of Leadership: Frame requests and reports in business terms, not just tech details.
-
Integrating AI-Based Automation
CIOs and ITSM leaders are now finding they need to integrate AI-based automation whenever it's possible and makes sense. It doesn't always. But, when it does, AI tools can improve automation, digital transformation, and overhaul time-consuming legacy systems. An example of this might be AI ticketing.
What You Can Do
Here are some simplified steps you can take to identify AI automation opportunities:
- Map Out Key Processes: List major workflows across departments and break them down into tasks.
- Spot Repetitive, Data-Driven Tasks: Look for steps that are manual, rule-based, or rely on pattern recognition.
- Evaluate Impact Potential: Prioritize tasks that waste time, cause delays, or hurt customer experience.
- Check Data Readiness: Provide clean, accessible data to support AI tools.
- Start Small with a Pilot: Test automation in one low-risk, high-value area before scaling.
- Collaborate Across Teams: Get input from IT, business units, and users to align on goals.
- Measure and Expand: Track results, refine the approach, and expand to other areas.
Lastly, be sure to ask vendors whether they'll be providing updated software with AI integrations.
-
Struggling with Legacy IT Systems and Outdated Support
The flip side of this is that some companies might be using outdated systems that are no longer going to be supported by vendors.
What You Can Do
If that's the case, ask yourself the following questions to determine whether to keep out-of-date technology or replace it with something better. Your company should evaluate based on cost, risk, performance, and strategic fit:
- Does it slow you down or hold you back?: Consider if it's impacting efficiency, innovation, or business goals.
- Is it costing more than it's worth?: Factor in maintenance, support, and workarounds vs. long-term value.
- Is it secure and compliant?: Outdated systems can increase cybersecurity risks and regulatory exposure.
- Can it integrate with other tools?: Poor compatibility creates silos and manual work, look for smarter options.
- Is it still supported?: If the vendor no longer updates it or offers support, you're exposed.
- Are users frustrated with it?: If it hurts productivity or morale, it's working against you.
- Would something newer give you a competitive edge?: Better tools may improve agility, service, and decision-making.
-
Internal and External Communication
The remote or hybrid work model train has left the station and is heading into the future full steam ahead, providing many benefits to employees and employers alike. For employers, it comes with enormous cost benefits. According to Business.com, savings to employers can average approximately $11,000 per year for every employee who works from home (WFH) at least 50% of the time.
For IT leaders, this means that internal and external communications have to align with this reality. This puts security and connectivity more prominently on an IT leader's radar and within budgetary planning. They need to make sure employees who aren't on-site are just as secure and connected as workers in the office. This can especially be when they're handling external customer-facing communications.
What You Can Do
Consider the following actions you can take to keep remote employees secure and connected:
- Secure Access: Use VPN, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and Single Sign-On for safe system access.
- Protect Devices: Provide secure company devices or enforce strong security for personal ones.
- Use Cloud Tools: Rely on cloud-based apps for file sharing, collaboration, and communication.
- Apply Zero Trust Principles: Limit access to only what's needed, and verify users and devices continuously.
- Train on Cybersecurity: Educate staff on phishing, safe browsing, and password best practices.
- Ensure Strong IT Support: Give remote teams access to reliable tech support and monitoring tools.
-
Managing Data and Data Security
Another remote-centric concern is about managing data and data security, especially when employees are WFH. Data security is always going to be a serious concern. It is even more relevant in 2025 when we factor in the danger of deepfake videos and emails within the cybersecurity matrix.
What You Can Do
Taking the following measures can help to effectively manage data and data security:
- Limit and Secure Access: Use role-based access, VPN, and MFA to protect systems and data.
- Protect Devices: Require encryption, antivirus, and endpoint security, whether devices are company-issued or personal.
- Centralize Data in the Cloud: Store files in secure, cloud-based platforms with access controls and backups.
- Set Clear Policies: Create and enforce rules for data handling, device use, and incident reporting.
- Train Your Team: Educate employees on threats like phishing and how to work securely from anywhere.
- Monitor and Respond: Use tools to track activity, detect issues, and respond quickly to any security events.
-
Managing Remote Teams
As CIOs know, and as stated above, remote and hybrid work isn't going away. Too many employees would prefer to work from home. Organizations that aren't happy with that are starting to lose talent to those who are offering remote/hybrid opportunities.
This means that ensuring remote systems are more secure and robust than ever is a concern for ITSM teams. This also has to involve improving security from fake and real internal threats and external cybersecurity dangers.
What You Can Do
- Use a Zero Trust Approach: Verify every user and device; limit access to only what's needed.
- Strengthen Login Security: Require MFA and strong passwords.
- Protect All Devices: Make sure all remote devices have encryption, antivirus, and regular updates.
- Monitor for Threats: Use tools to detect unusual behavior from insiders and external attackers.
- Secure Cloud and Collaboration Tools: Limit permissions, block risky sharing, and monitor app usage.
- Control Sensitive Data: Prevent unauthorized downloads, sharing, or transfers with data loss prevention tools.
- Train Employees: Teach staff to spot phishing, deepfakes, and other social engineering threats.
- Be Ready to Respond: Keep a remote-specific incident response plan updated and tested.
-
Maintaining Business Continuity
Business continuity is another ITSM-related issue.
IT leaders need to have redundancies and safeguards in place in the event of an IT disaster or other issue that could affect operational practices. Have you road-tested your most recent IT business continuity plan, and IT disaster plan? If not, now is the time to get prepared for 2025 and beyond.
What You Can Do
- Back Up Data Regularly: Use automated, off-site, and cloud backups, and test them often.
- Build System Redundancy: Set up failover systems, backup servers, and internet to stay online during outages.
- Have a Clear Continuity & Recovery Plan: Document how to keep operations running and recover critical systems fast (define Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO).
- Protect Against Cyber Threats: Use firewalls, endpoint security, and access controls to prevent and contain attacks.
- Prepare Communication Channels: Have multiple ways to reach employees, customers, and vendors during disruptions.
- Assign Roles and Train Teams: Designate responsibilities and make sure backups are ready to step in if needed.
- Choose Resilient Vendors: Work with cloud/SaaS providers who offer strong uptime and disaster recovery.
- Test and Improve Regularly: Run drills to prove plans work and update them as needed.
-
Complex IT Systems, SaaS Tech Bloat
Too many organizations are juggling overly complicated and often redundant layers of IT systems and SaaS vendor relationships.
Aim to make sense of your bloated IT jungle in 2025. This can help you clearly see what everyone is using and where cost-cutting and consolidations can be implemented. It's also useful from a security perspective, to help make sure the software team members are using is up-to-date and as secure as possible.
What You Can Do
- List Everything: Create a complete inventory of all systems and SaaS tools, including cost and usage.
- Spot Redundancies: Identify overlapping tools or underused subscriptions.
- Map Tools to Business Needs: Make sure each tool supports a clear function or goal.
- Check Integration: Look for systems that don't work well together or cause manual workarounds.
- Get User Feedback: Ask teams what tools they actually use, and which ones they don't.
- Consolidate and Eliminate: Keep what's essential, cut what's not, and standardize where possible.
- Audit Costs and Contracts: Review expenses, user counts, and renewal terms to reduce waste.
- Set Clear Governance: Define policies for buying, using, and reviewing tech going forward.
-
Managing SaaS Vendor Relations
With dozens or hundreds of vendors in a tech stack comes increasingly complex vendor relations. Managing all of this, alongside the actual cost, is the price organizations pay for tech bloat. This includes numerous interrelated integrations, software overlaps, and needing to contact support if anything goes wrong.
What You Can Do
- Centralize SaaS Visibility: Maintain a single, up-to-date inventory of all SaaS tools, including owners, costs, usage, and renewal dates.
- Assign Ownership: Make someone accountable for each tool who can justify its purpose and usage.
- Evaluate Usage Regularly: Track license usage, user activity, and ROI. Cancel or scale down underused subscriptions.
- Consolidate Tools Where Possible: Replace niche or overlapping apps with broader platforms that serve multiple functions (e.g., Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, Notion).
- Standardize Procurement: Route all new SaaS purchases through IT or procurement for vetting and approval, no more "shadow IT."
- Negotiate Smarter Contracts: Consolidate licenses across teams for volume discounts and use annual reviews to renegotiate terms or reduce unused seats.
- Set Governance Policies: Create clear guidelines for tool selection, renewal approval, data security, and integration standards.
- Educate Departments: Help teams understand the impact of unnecessary tools and how smarter SaaS choices support security, budget, and productivity.
-
Data Protection and Privacy
Data protection and privacy are more important now than ever before. Organizations are facing increasing cybersecurity threats, and in most cases, criminals want access to customer data. Thanks to AI bots and deepfake content, it's now more affordable to try and cyberattack large and mid-size organizations.
As a result, IT leaders need to invest more in cybersecurity and training to keep sensitive customer data protected and secure from internal and external threats.
What You Can Do
- Protect the Data First: Focus security tools and policies around sensitive customer data using encryption and access controls.
- Build Strong, Layered Defenses: Use firewalls, MFA, endpoint protection, and advanced threat detection tools like EDR/XDR.
- Limit and Verify Access: Apply Zero Trust principles where no one gets access without verification and clear need.
- Train Everyone Often: Run regular security training and phishing simulations for all staff, including remote and third-party users.
- Watch for Insider Threats: Teach employees how to recognize and report suspicious activity, inside and out.
- Test and Improve Constantly: Perform audits and risk assessments regularly, and use the results to strengthen systems and training.
- Align with Regulations: Verify security efforts meet compliance standards like HIPAA, GDPR, or SOC 2.
- Make Security a Business Priority: Involve leadership, fund cybersecurity proactively, and treat it as critical infrastructure.
-
Lack of Change Management Strategy
Despite software, cloud computing, apps, and AI being everywhere, there's a surprising lack of change management strategy in larger organizations. And this usually includes healthcare and insurance, and other sectors that have been slow to adapt to changing times.
IT leaders and CIOs need to take advantage of exciting new change management opportunities to make sure they're not left behind in 2025.
What You Can Do
- Align with Business Goals: Make sure every change supports key objectives and involves the right stakeholders.
- Standardize the Process: Use a clear, consistent framework for submitting, approving, and implementing changes.
- Assess Risk and Impact: Evaluate changes based on risk, urgency, and dependencies before moving forward.
- Communicate Early and Clearly: Keep teams informed about what's changing, why, and when, and collect feedback.
- Measure Results: Track outcomes, fix issues quickly, and use what you learn to improve future changes.
- Balance Speed and Stability: Fast-track low-risk changes, but apply tighter controls to complex ones.
- Automate Where It Helps: Use tools to automate IT processes and streamline approvals, notifications, and tracking.
- Build Change Readiness: Train teams to adapt smoothly and treat change as a normal part of growth.
-
Shadow AI and Unapproved Tool Usage
As AI tools become more accessible (e.g., ChatGPT, GitHub Copilot), employees may use them without IT oversight, posing data leakage and compliance risks.
What You Can Do
Create policies for AI tool usage, implement monitoring, and educate users on risks.
-
AI Governance and Ethical Use
IT leaders must now show that AI tools are explainable, fair, and compliant, especially when used in customer-facing or HR-related applications.
What You Can Do
Establish AI usage standards, define acceptable use, and ensure Large Language Models (LLMs, used in AI "understanding") outputs are traceable and auditable.
Conclusion: Overcoming IT Challenges for Business Success
In 2025, IT challenges go beyond just fixing technical problems — they affect how a business runs, serves customers, and plans for the future. Technology is changing fast, and IT leaders need to stay flexible, make smart decisions, and plan ahead. Solving these challenges isn't just about avoiding problems — it's also an opportunity to improve systems and help the whole organization work better.
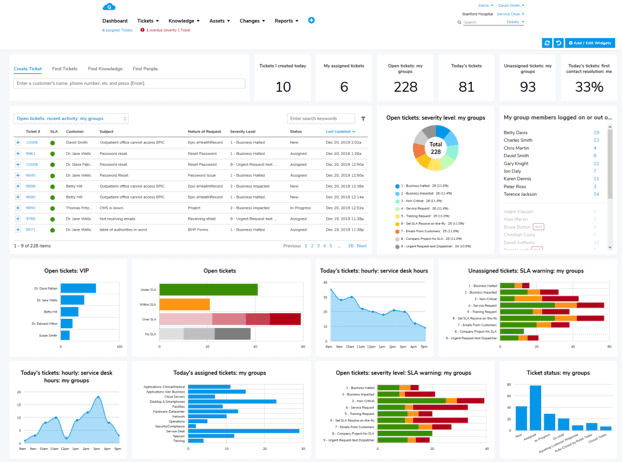
Giva Can Help Streamline Your Help Desk Operations
Giva has a suite of SaaS support applications for IT teams including:
Giva helps teams achieve Service Management excellence:
- Deploy in days, train in 1 hour
- Robust, fast & painless reporting for higher-quality decision-making
- Highly customizable without programming or consultants
Get a demo to see Giva's solutions in action, or start your own free, 30-day trial today!